Apr
Interesting Facts of Internationalization & Localization testing
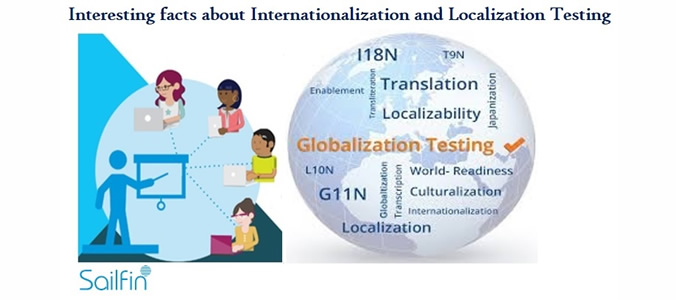
Thereby, Localization can be called a subset of Internationalization. What are the steps for Globalization process? 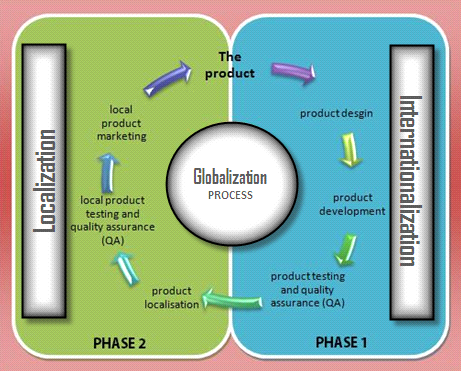 As highlighted in above flowchart, internationalization and localization can be divided into two phases. Phase 1 includes the planning and preparation for a product which is built to support global markets. During this phase, all locale specific references should be removed to ease the localization of the product which if done later in Phase 2, causes waste of time and money. Phase 2 includes the adaptation of the product for a locale using regional specific spellings, terms, weights, measures etc.
As highlighted in above flowchart, internationalization and localization can be divided into two phases. Phase 1 includes the planning and preparation for a product which is built to support global markets. During this phase, all locale specific references should be removed to ease the localization of the product which if done later in Phase 2, causes waste of time and money. Phase 2 includes the adaptation of the product for a locale using regional specific spellings, terms, weights, measures etc.
At the end, each phase includes minute and thorough testing to ensure that the product meets the expectations of end users across the globe. Best example to explain internationalization and localization For the very first time, Google had launched its engine in its native English language. Later Google introduced different languages for its search engine and now, Google supports 123 different languages. This shows how Google adapted internationalization after conquering market in a single language to make the search engine robust across the globe. Scope of internationalization and localization testing Some of the critical points to be covered in localization and internationalization testing: 1) Language
- Number systems
- Spelling variations
- Writing directions
- Layouts and Keyboard shortcuts
- Capitalization and sorting rules
2) Culture and region
- Names and titles
- Telephone numbers, zip codes, Address formats
- Colors and images
- Currency symbol and currency market position
- Weights and measures
3) Dates and Notable Events
- Date and time formats
- Calendar types (Iranian, Egyptian, Gregorian etc.)
- Number formats (grouping of digits, decimal separators etc.)
Benefits of internationalization and localization testing
- Visibility of the product across the globe.
- Cost effective compared to its robust behavior.
- Overall testing costs reduces.
- Guarantees a more flexible and scalable application.
- Source code for the product becomes robust.
- Maintenance becomes simpler.
- Quality of code and architecture of overall product improvises
Challenges of internationalization and localization testing
- Salesforce application – some text could not be translated from translation workbench. Runtime error messages, pop ups had to be handled through custom labels.
- Some translations behave differently or don’t get translated across all supported browsers in a uniform manner. Mostly translation issues are found in IE browser.
- Alignments, formatting, numbering related issues are also common.
I hope this gives you some great insights on the specific testing process needed for these specialized scenarios. Happy Reading!